Pandas, why is it fast?
Pandas
Pandas is a very useful tool for data munging. Pandas is efficient in handling column operations. The secret for its speed is that internally data is stored as numpy arrays in Fortran order. I will explain why pandas is faster.
Memory access of columns
Consider the 2D array,
arr = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
The data looks like this
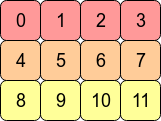
C order is row major order. Fortran order is column major order.
In C order, the data is stored like this RAM. This arr is C contiguous.

In Fortran order, the data is stored like this in RAM. This arr is Fortran contiguous.
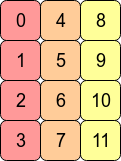
One should know that it is very fast to access immediate locations in RAM. Accessing each element in a row is very fast in C order. Accessing each element in a column is very fast in Fortran order.
Speed
Since data scientists need to work on columns often, pandas works very fast for data munging.
(The same thing can be achieved by using numpy arrays in fortran order. But it’s just lot of book keeping.)
This is also a reason why DataFrame.apply and DataFrame.map are considerably slower than column operations.
You can create a dataframe with C-order. But it won’t give good speed for column operations.
df = pd.DataFrame(np.ascontiguousarray(df.values), columns=df.columns, copy=False)
You can print to check if the numpy array is Fortran/C contiguous.
print(df.values.flags)
